Estimated reading time: 0 minutes
The escalating global epidemic of obesity brings to light its extensive health repercussions, especially its profound influence on liver function. This complex interplay of obesity, insulin resistance, and liver health deterioration poses a significant public health dilemma. Grasping the intricate dynamics among these elements is vital for formulating strategies that effectively interrupt this cycle, ensuring the preservation of liver health.
Exploring the Complex Web of Obesity, Insulin Resistance, and Liver Health
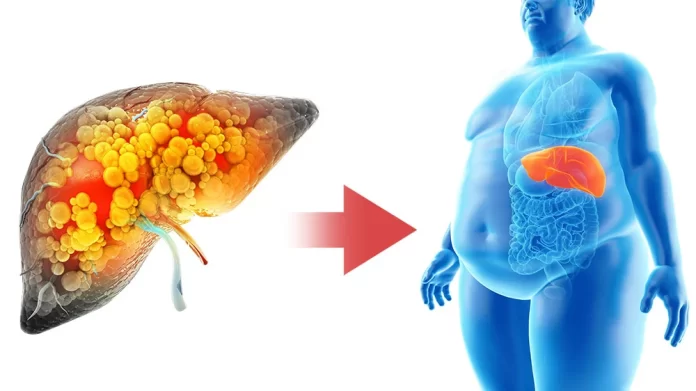
1. Obesity’s Influence on Liver Conditions: Marked by an excessive accumulation of body fat, obesity stands as a critical factor in the onset of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), the predominant liver disorder worldwide. This condition spans from simple steatosis, characterized by fat accumulation, to Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH), and potentially advances to cirrhosis and liver cancer.
2. Insulin Resistance at the Core: At the heart of the relationship between obesity and liver complications lies insulin resistance. This scenario emerges when cells become less responsive to insulin, a situation often triggered by obesity. As a consequence, the pancreas is prompted to overproduce insulin, leading to hyperinsulinemia, which further perpetuates weight gain and fosters a self-sustaining cycle. Moreover, insulin resistance encourages the liver to ramp up glucose output and lipid synthesis, culminating in fat accumulation within the liver.
3. The Consequences of Inflammation and Oxidative Stress: The state of obesity initiates chronic low-grade inflammation and oxidative stress, which exacerbates insulin resistance and liver damage. These conditions not only fast-track liver disease progression but also amplify the risk of developing additional metabolic disorders, such as type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular diseases.
Initiatives to Disrupt the Cycle
1. Pursuing Lifestyle Changes for Weight Reduction: Addressing this cycle demands significant lifestyle adjustments focused on achieving and maintaining optimal weight. Adopting a diet centered on whole, unprocessed foods and a balanced intake of macronutrients, along with regular physical activity, can markedly decrease body fat and enhance insulin sensitivity.
2. Pharmacological Management of Insulin Resistance: In certain instances, drug interventions become essential for controlling insulin resistance and alleviating its impact on liver health. Drugs like metformin, traditionally prescribed for managing type 2 diabetes, have demonstrated efficacy in enhancing insulin sensitivity and diminishing liver fat content.
3. Regular Liver Health Assessments: For those at risk or already diagnosed with NAFLD, consistent monitoring of liver functionality through laboratory tests and imaging is crucial. Timely detection and management can halt the disease’s progression and minimize the chances of encountering severe complications.
4. Boosting Education and Public Awareness: Increasing public awareness regarding the interconnection between obesity, insulin resistance, and liver health is fundamental for preventive measures. Public health campaigns that advocate for nutritional education, active lifestyles, and healthy living can significantly deter the obesity epidemic and its adverse effects on liver health.
Summary
The intertwined relationship among obesity, insulin resistance, and liver health highlights the necessity for a multifaceted approach in tackling these interconnected issues. Through lifestyle changes, appropriate medical interventions, and heightened awareness, it’s feasible to interrupt the cycle of obesity and insulin resistance, thus safeguarding liver health and promoting overall wellness. The collaborative engagement of healthcare professionals, policymakers, and the community is indispensable in addressing the surge in obesity and its detrimental impact on liver disease and metabolic health.
Related-
Know More About Ayurveda Treatments For Liver Related Disorders.
GET IN TOUCH

Recent comments