Navigating the Intersection of Psoriasis and Crohn’s Disease: An Integrative Approach
Introduction
Psoriasis and Crohn’s Disease (CD) are chronic inflammatory disorders that impact the skin and gastrointestinal tract, respectively. Despite affecting different areas of the body, these conditions share common underlying mechanisms such as genetic predispositions, immune system dysregulation, and environmental triggers. Understanding the connection between psoriasis and CD can lead to more effective management strategies and improved patient outcomes. This article examines the interrelationship between these two diseases, their shared pathophysiology, clinical implications, and integrative treatment approaches.
Overview of Psoriasis and Crohn’s Disease
Psoriasis
Nature:
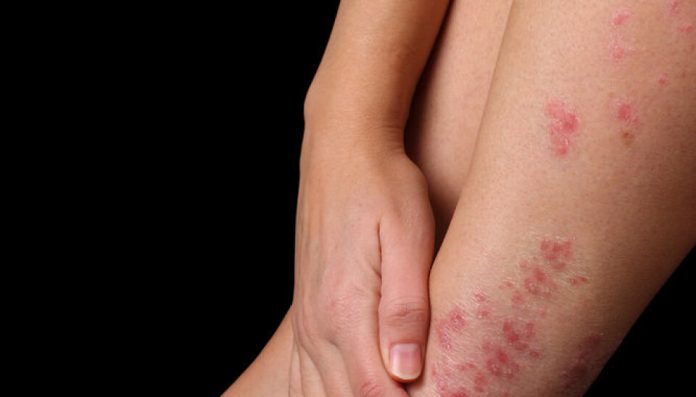
- Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disorder characterized by the presence of red, scaly patches, typically found on the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back.
- The condition results from an accelerated skin cell growth cycle, causing an accumulation of cells on the skin’s surface.
Pathophysiology:
- Immune Dysregulation: T-cells mistakenly target healthy skin cells, triggering inflammation and rapid skin cell turnover.
- Genetic Factors: A family history of psoriasis increases the likelihood of developing the condition.
- Environmental Triggers: Stress, infections, and certain medications can exacerbate psoriasis.
Crohn’s Disease (CD)
Nature:
- CD is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) characterized by chronic inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract, most commonly affecting the ileum and colon.
- Symptoms include abdominal pain, diarrhea, weight loss, and fatigue.
Pathophysiology:
- Immune System Dysfunction: An abnormal immune response leads to inflammation in the digestive tract.
- Genetic Factors: Genetic predispositions are significant in the development of CD.
- Environmental Triggers: Factors such as diet, stress, and smoking can worsen CD symptoms.
The Connection Between Psoriasis and Crohn’s Disease
Shared Pathogenic Mechanisms
Genetic Links:
- Both conditions are associated with specific genetic markers, such as mutations in the IL23R gene, which plays a crucial role in immune response regulation.
Immune System Dysregulation:
- Psoriasis and CD involve an overactive immune system, leading to chronic inflammation. Key cytokines like TNF-alpha, IL-17, and IL-23 are implicated in both diseases.
Microbiome Influence:
- The gut microbiome plays a vital role in systemic inflammation. Dysbiosis, or an imbalance in gut bacteria, has been linked to both psoriasis and CD.
Clinical Implications
Symptom Overlap:
- Patients with CD may develop psoriatic lesions, while those with psoriasis might experience gastrointestinal symptoms.
Increased Morbidity:
- The co-existence of these conditions can lead to more severe symptoms, increased complications, and a reduced quality of life.
Research Insights:
- Studies indicate that individuals with one condition are at a higher risk of developing the other. For example, patients with psoriasis have a greater likelihood of developing CD, and vice versa.
- Clinical observations suggest that addressing one condition may positively impact the other due to the shared inflammatory pathways.
Integrative Treatment Strategies
Modern Medical Treatments
Biologics:
- Medications like TNF-alpha inhibitors (e.g., infliximab, adalimumab) effectively target key inflammatory pathways common to both psoriasis and CD.
Immunosuppressants:
- Drugs such as methotrexate and cyclosporine help control inflammation in both conditions.
Lifestyle Modifications:
- Dietary adjustments, smoking cessation, and stress management are crucial for managing both psoriasis and CD.
Ayurvedic Approaches
Dietary Adjustments:
Balancing Doshas:
- Tailoring the diet to balance Vata, Pitta, and Kapha doshas is essential for improving skin and gut health.
Relevant Shloka: “Pathya ahara vihara sevana”
(Charaka Samhita, Sutrasthana 30.26)
“Consumption of a suitable diet and lifestyle is essential.”
Recommended Foods:
- Anti-inflammatory foods such as turmeric, ginger, and leafy greens, while avoiding spicy, oily, and processed foods.
Herbal Remedies:
- Neem (Azadirachta indica): Known for its anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties, beneficial for both skin and gut health.
- Turmeric (Curcuma longa): Reduces systemic inflammation and supports immune regulation.
- Guduchi (Tinospora cordifolia): Acts as an immunomodulator, helping to balance the immune response and reduce inflammation.
Lifestyle Adjustments:
Stress Management:
- Incorporating practices like yoga, meditation, and pranayama (breathing exercises) to reduce stress and improve overall well-being.
Regular Exercise:
- Physical activity supports digestion, lowers systemic inflammation, and enhances mental health.
Relevant Shloka: “Yogah chittavritti nirodhah”
(Yoga Sutras of Patanjali 1.2)
“Yoga is the cessation of the fluctuations of the mind.”
Case Studies: Integrative Management of Co-existing Conditions
Case Study 1: Managing Psoriasis and Crohn’s Disease
Patient Profile:
- Name: Alex P.
- Age: 40
- Symptoms: Chronic psoriatic lesions on the scalp and elbows, abdominal pain, and frequent diarrhea.
Integrative Treatment Plan:
Modern Medical Approach:
- Biologics: Use of adalimumab to manage both psoriasis and CD.
- Dietary Changes: Implementation of a low-inflammatory diet and smoking cessation.
Ayurvedic Approach:
- Dietary Modifications: A Pitta-pacifying diet with cooling and anti-inflammatory foods.
- Herbal Support: Neem and turmeric supplements to reduce inflammation and support immune health.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Incorporating yoga and meditation to manage stress and enhance overall well-being.
Outcome:
- Significant reduction in psoriatic lesions and gastrointestinal symptoms, improved energy levels, and enhanced quality of life.
Case Study 2: Holistic Management of Co-existing Conditions
Patient Profile:
- Name: Sarah L.
- Age: 35
- Symptoms: Severe psoriasis with extensive skin involvement, chronic abdominal pain, and weight loss.
Integrative Treatment Plan:
Modern Medical Approach:
- Immunosuppressants: Administration of methotrexate to control inflammation.
- Nutritional Support: A balanced diet with adequate nutrients to address weight loss.
Ayurvedic Approach:
- Dietary Modifications: A Vata and Pitta-pacifying diet to reduce inflammation and support gut health.
- Herbal Support: Guduchi and turmeric to balance the immune response and alleviate inflammation.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Daily practice of yoga and pranayama to improve mental and physical health.
Outcome:
- Reduced severity of psoriasis, improved gastrointestinal symptoms, better skin condition, enhanced digestion, and stabilized weight.
Conclusion
The co-occurrence of psoriasis and Crohn’s Disease presents a complex clinical challenge that requires a comprehensive, integrative approach to treatment. By understanding the shared pathogenic mechanisms and addressing both skin and gut health through modern medical therapies and Ayurvedic practices, patients can experience significant improvements in their symptoms and overall well-being.
For those seeking a personalized, integrative approach to managing psoriasis and Crohn’s Disease, EliteAyurveda Specialist Clinic offers tailored treatment plans designed to restore balance and promote health. Visit EliteAyurveda to learn more about our holistic treatments and expert care. Embrace the combined wisdom of Ayurveda and modern medicine for effective management and long-term relief from chronic inflammatory conditions.
Related-
Know More About Ayurveda Treatments for Dermatology.
GET IN TOUCH

Recent comments