Estimated reading time: 0 minutes
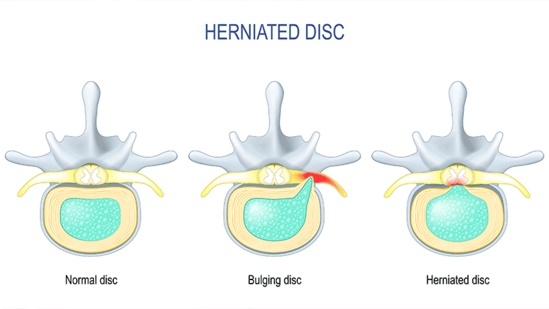
If a disc in your lower spine bulges or tears, you might experience pain in your lower back and/or limb. Here are three distinct signs of a herniated or distended disc to help you determine the root cause of your lower back pain:
1. Sitting discomfort
Sitting places a great deal of stress on your lower spinal discs. If you have a herniated or bulging disc, the increased pressure within your disc may cause the protrusion to become more pronounced as you sit, causing your lower back pain to worsen.
2. Radiated pain down the leg (sciatica)
Discs in the lower back typically herniate or bulge in the posterior (back) and/or lateral (side) region, near to the spinal nerve roots. These nerve origins can be harmed by herniated discs in one or both of the following ways:
Compression that is directly applied. When the interior contents of a bulging or leaking disc immediately impinge on a spinal nerve root as it exits the spinal canal.
Chemically-induced irritation. The region surrounding the nerve root may become inflamed and irritated when a herniated disc leaks corrosive chemical irritants.
You may experience burning pain, paralysis, weakness, and/or tingling along the front and/or back of your thigh, leg, and/or foot as a result of a damaged nerve root. The medical term for these symptoms is sciatica. Typically, sciatica symptoms and signs affect only one limb at a time.
3. Pain made worse by certain activities
Certain activities, including those listed below, may aggravate your lower back pain and/or sciatica.
Downward/forward twisting
Lifting a heavy object while endeavouring to push or move it.
Sneezing and wheezing are symptoms of a cold.
Disc herniation in the lumbar region is typically accompanied by an abrupt onset of pain. In the majority of instances, there is no apparent cause of pain, such as an injury or traumatic event. Despite this, the suffering feels abrupt.
This disease can be excruciatingly agonising, but its symptoms are typically brief. Even if they did not receive medical treatment, approximately 90% of people with acute lumbar disc herniation report that the discomfort has subsided within six weeks.
When to seek medical care and when to avoid it
Consult your physician if any of these three symptoms of a displaced disc are present. In order to reduce inflammation and alleviate pain, your doctor may recommend a combination of nonsurgical treatments, such as anti-inflammatory medications and a guided physical therapy programme, as well as a referral to an interventional pain specialist for image-guided lumbar injections.
Consult your physician immediately if you experience difficulty controlling your bowel and/or bladder movements, paralysis in your inner thigh and genital area, or difficulty starting to urinate. These symptoms and signs may indicate cauda equina syndrome, a serious medical emergency that can result from severe disc herniations in the lower back.
Related-
Know more about Ayurvedic Spinal Disk & Radiculopathy Treatments.
GET IN TOUCH

Recent comments